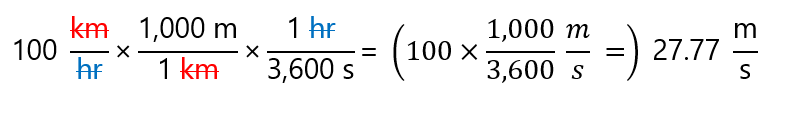Factor label method (also called unit factor method or dimensional analysis) is a useful tool in science. Once you know it, you will find that many problems can be easily solved.
It handles the units or labels in the same way that we do with numbers. It is based on the creation of relationships between quantities that are proportional to each other. For example, 1,000 m = 1 km. We can express it as:
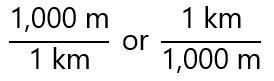
Let’s start with an easy example, in fact, it is so easy that you could do directly, but it will help to clarify the steps. Let’s transform 5 km to m, using the factor label method. As the change is km → m, from the relationships given above, I choose the one that gives “m/km” (you will see soon why) and write:
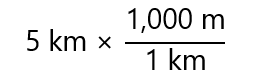
As km appears in the numerator and denominator of the units, they cancel each other (that is the reason of choosing “m/km”, as ,choosing “km/m” will not cancel km)
This has been very easy, I know. Let’s do something more difficult convert 100 km/hr to m/s. This means, that we want to transform km to m and hr to s, to do that, we need the equivalence between these units:
- As 1,000 m = 1 km, we will use (again) one of these expressions:
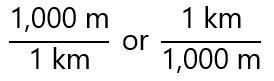
- As 3,600 s = 1 hr, we will use one of these expressions:
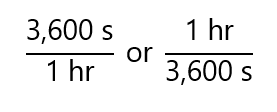
We are doing by steps:
- Convert from km to m:
- The expression is 100 km/hr
- We need to replace km (in the numerator) by m (also in the numerator), so I will use the previous expression 1,000 m/1 km and write:
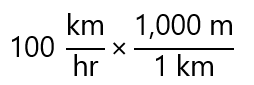
-
- As km appears in the numerator and in the denominator of the multiplication, they cancel each other (careful, only the units, not the numbers) and write:
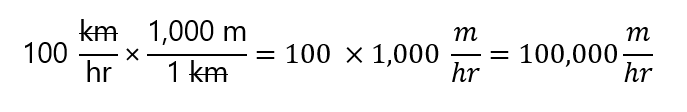
-
- In this way, the km has been converted into m.
- Convert from hr to s:
- We have 100,000 m/hr
- We need to replace ‘hr’ I the denominator by ‘s’ (also in the denominator), so I will use the expression 1 hr/3,600 s
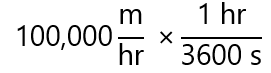
-
- As hr appears in the denominator and in the numerator of the multiplication, they cancel each other:

In reality, you do all in one step, just make sure that the units are cancelled each other: